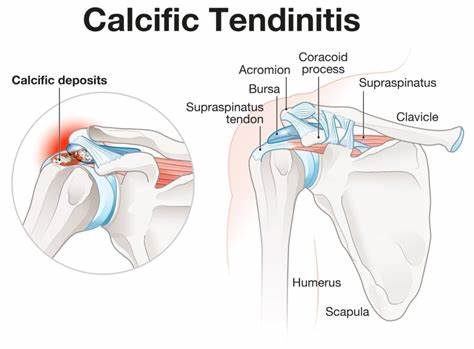
Calcific tendonitis is a painful condition that affects the shoulder joint, causing discomfort and restricted movement. It occurs when calcium deposits build up in the tendons of the shoulder, leading to inflammation and pain. While it can be debilitating, understanding its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention measures can help individuals manage this condition effectively.
What is Calcific tendonitis?
Calcific tendonitis:
Calcific tendonitis, also known as calcific tendinopathy, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of calcium deposits within the tendons of the shoulder joint. These deposits can form over time and cause irritation, inflammation, and pain. The condition typically affects individuals between the ages of 30 and 50, although it can occur at any age.
Causes :
The exact cause of calcific tendonitis is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Age: As individuals age, the tendons in the shoulder joint may degenerate, making them more susceptible to calcium deposits.
- Overuse or Repetitive Stress: Activities that involve repetitive overhead movements, such as throwing, swimming, or lifting heavy objects, can strain the tendons and lead to the formation of calcium deposits.
- Poor Blood Circulation: Reduced blood flow to the tendons may impair the body’s ability to clear calcium deposits, allowing them to accumulate and cause inflammation.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing calcific tendonitis.
Symptoms :
The symptoms of calcific tendonitis can vary from mild to severe and may include:
- Pain: Persistent pain in the shoulder joint, which may worsen with movement or pressure on the affected area.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the shoulder joint, especially when lifting the arm or reaching overhead.
- Swelling: Swelling and tenderness around the shoulder joint.
- Decreased Range of Motion: Limited range of motion in the shoulder, making everyday activities challenging.
- Weakness: Weakness in the shoulder muscles due to pain and inflammation.
What are differential diagnosis for calcific tendonitis in shoulder joint?
Differential diagnosis:
Differential diagnosis of calcific tendonitis in the shoulder joint typically includes:
- 1. Rotator cuff tendinopathy: Inflammation or degeneration of the rotator cuff tendons.
- 2. Shoulder impingement syndrome: Compression of the rotator cuff tendons and bursa in the subacromial space.
- 3. Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis): Painful and restricted range of motion due to inflammation and thickening of the shoulder joint capsule.
- 4. Glenohumeral osteoarthritis: Degeneration of the cartilage in the shoulder joint.
- 5. Biceps tendinopathy: Inflammation or degeneration of the long head of the biceps tendon.
- 6. Subacromial bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa located between the acromion and rotator cuff tendons.
- 7. Labral tear: Injury to the ring of cartilage (labrum) surrounding the shoulder socket.
- Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD): Deposition of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in the joint, causing inflammation and pain.
- 9. Rheumatoid arthritis: Autoimmune condition affecting the joints, including the shoulder.
- Septic arthritis: Infection of the shoulder joint, leading to inflammation and pain.
What is a treatment plan for calcific tendonitis?
Treatment Options:
Treatment for calcific tendonitis aims to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and improve shoulder function. The approach may vary depending on the severity of the symptoms and may include:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate the symptoms and resting the shoulder joint can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Gentle exercises and stretches prescribed by a physical therapist can help improve shoulder mobility and strengthen the surrounding muscles.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injections of corticosteroids into the shoulder joint can help reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief from pain.
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT): ESWT is a non-invasive treatment that uses shock waves to break up the calcium deposits in the tendons, promoting healing.
- Ultrasound-Guided Needle Aspiration: In some cases, a healthcare provider may use ultrasound guidance to aspirate or remove the calcium deposits from the shoulder tendons.
- Surgery: In severe cases where conservative treatments have failed, surgery may be necessary to remove the calcium deposits or repair damaged tendons.
What is physical therapy treatment plan for calcific tendonitis in shoulder joint?
Physical therapy:
Here’s a general physical therapy plan for calcific tendonitis in the shoulder joint:
- Pain Management: Initially, focus on reducing pain and inflammation through modalities like ice therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation.
- Range of Motion Exercises: Gentle exercises to improve shoulder mobility without exacerbating pain. These may include pendulum exercises, wand exercises, or passive range of motion stretches.
- Stretching: Gradually introduce stretching exercises to improve flexibility and decrease stiffness in the shoulder joint and surrounding muscles.
- Strengthening Exercises: Begin with low-resistance exercises targeting the rotator cuff muscles and other shoulder stabilizers. As tolerance improves, progress to higher resistance exercises.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as soft tissue massage, joint mobilizations, and stretching administered by a physical therapist can help break up calcifications and improve tissue mobility.
- Functional Training: Incorporate activities that mimic daily tasks or sports-specific movements to improve overall shoulder function and performance.
- Posture Correction: Address any postural issues that may contribute to shoulder pain and dysfunction, such as rounded shoulders or forward head posture.
- Education and Home Exercise Program: Teach proper body mechanics, ergonomics, and provide a home exercise program to reinforce gains made during therapy sessions.
- Activity Modification: Advise on modifying activities or movements that aggravate symptoms to prevent further irritation of the shoulder joint.
- Gradual Return to Activities: Once pain is under control and strength and flexibility have improved, gradually reintroduce activities and sports while monitoring for any signs of recurrence.
What type of exercises are best for calcific tendonitis in shoulder joint?
Exercises:
Exercises for calcific tendonitis in the shoulder joint typically focus on stretching and strengthening the muscles around the shoulder to improve mobility and reduce pain. Here are some recommended exercises:
Pendulum stretch:
The pendulum stretch can be a helpful exercise for managing pain and stiffness associated with calcific tendonitis of the shoulder. It is a passive stretch, meaning you use gravity to move your arm rather than actively contracting muscles. This is important during the early stages of calcific tendonitis, as active stretching can irritate the inflamed tendon.
How to perform:
Here’s how to perform the pendulum stretch:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Lean forward and rest your unaffected hand on a sturdy surface, such as a table or chair.
- Allow your affected arm to hang loosely by your side.
- Gently swing your arm back and forth in small circles. You can also swing your arm forward and backward, or side to side.
- Focus on keeping your shoulder muscles relaxed throughout the movement.
- Continue for 30 seconds to 1 minute.
- Repeat 3-5 times per day.
Additional Tips:
- If you feel any pain during the stretch, stop immediately and consult with your doctor or physical therapist.
- You can increase the range of motion of the swing gradually as your pain improves.
- It is important to maintain good posture throughout the exercise. Avoid hunching your back or rounding your shoulders
Shoulder blade squeeze:
This exercise, also known as shoulder retraction, strengthens the muscles that stabilize the shoulder blade and improve posture. Stronger muscles can help reduce inflammation and pain in the shoulder joint.
How to perform:
Here’s how to perform a shoulder blade squeeze:
- Sit or stand with good posture, your back straight and shoulders relaxed.
- Gently squeeze your shoulder blades together, drawing them down toward your spine. You should feel your shoulder muscles engage.
- Hold the squeeze for 5 seconds, then relax.
- Repeat 10 times.
Additional Tips:
Here are some additional tips for performing shoulder blade squeezes:
- Don’t shrug your shoulders. The movement should come from your shoulder blades, not your shoulders.
- Don’t arch your back. Keep your back straight and your core engaged.
- Breathe normally throughout the exercise.
- If you feel any pain, stop the exercise.
External rotation stretch:
External rotation stretches may not be the most appropriate exercise for calcific tendonitis in the shoulder, especially in the acute phase. This is because external rotation can compress the subacromial space, where the inflammation is likely occurring. However, gentle passive external rotations prescribed by a physical therapist can be helpful in improving range of motion once the inflammation has subsided.
Other stretches:
Here are some safer stretches for calcific tendonitis:
- Doorway passive stretch: Stand in a doorway and place your forearms on either side of the door frame at elbow height. Lean forward gently until you feel a stretch in your chest. Hold for 15-30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times.
- Pendulum stretch: Stand with your knees slightly bent and lean forward, letting your affected arm hang loosely beside you. Sway your body back and forth gently, allowing your arm to swing freely. Repeat for 30 seconds.
- Posterior capsule stretch: Lie on your back with a rolled-up towel placed lengthwise between your spine and shoulder blades. Bend your knees and bring your affected arm overhead. With your other hand, gently pull your affected arm down towards your chest until you feel a stretch in the back of your shoulder. Hold for 15-30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times
Internal rotation stretch:
You should consult with a doctor before starting any new exercises, especially for a condition like calcific tendonitis. Internal rotation stretches can be helpful for increasing range of motion in the shoulder, but they may not be appropriate for everyone with this condition.
How to perform:
Stand with your affected arm behind your back and reach up towards your opposite shoulder blade. Use your other hand to gently push your elbow further up your back until you feel a stretch. Hold for 15-30 seconds, then release. Repeat several times.
Doorway passive internal rotation stretch:
- Stand in a doorway with your injured arm closest to the doorjamb.
- Bend your elbow to 90 degrees, with your hand flat against the doorjamb at shoulder height.
- Gently lean your upper body away from the doorway, keeping your elbow bent and your arm against the doorjamb. You should feel a stretch in the front of your shoulder.
- Hold for 15-30 seconds, then relax.
- Repeat 2-3 times.
Additional Tips:
Here are some additional tips for performing this stretch:
- Do not push into pain. If you feel any pain, stop the stretch and consult with your doctor.
- Breathe slowly and evenly throughout the stretch.
- You can use a strap or towel to assist you with this stretch if needed. Loop the strap or towel around your wrist and the top of the doorjamb, and gently pull on the strap to deepen the stretch.
Ys and Ts:
Ys and Ts exercises can be helpful for improving strength and stability in your shoulder muscles, which can aid in managing calcific tendonitis. Here’s how to perform them:
How to perform:
- Lie on your stomach with your palms flat on the floor and your elbows bent at 90 degrees.
- Lift your upper body off the floor, keeping your arms straight and your thumbs pointing up towards the ceiling (Y position).
- Lower yourself back down to the starting position.
- Spread your arms out to the sides, keeping your elbows bent and your thumbs pointing out to the sides (T position).
- Lower yourself back down to the starting position.
- Alternate between Y and T positions for 10 repetitions each.
Additional Tips:
- Maintain good form throughout the exercise. Don’t arch your back or hyperextend your elbows.
- Breathe normally during the exercise.
- Stop if you feel any pain and consult a healthcare professional.
Neck stretches:
While neck stretches themselves won’t directly address calcific tendonitis in the shoulder, they can improve tightness and discomfort in the neck and upper back muscles, which can sometimes refer pain to the shoulder. Here are two gentle neck stretches you can try:
Chin tuck stretch:
- Sit or stand with good posture.
- Slowly tuck your chin down towards your chest, lengthening the back of your neck.
- Hold for 15-30 seconds, then slowly relax.
- Repeat 3-5 times.
Lateral neck stretch:
- Sit or stand with good posture.
- Gently tilt your head to one side, bringing your ear towards your shoulder. You can use your hand to provide gentle assistance.
- Hold for 15-30 seconds, then slowly relax and repeat on the other side.
- Repeat 3-5 times on each side.
Important note:
- If you experience any pain during these stretches, stop immediately and consult with a healthcare professional.
- These stretches are meant to be gentle. Don’t force any movement.
How to prevent Calcific Tendonitis?
Prevention Measures:
While calcific tendonitis may not always be preventable, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing the condition:
- Maintain Proper Posture: Practicing good posture can help prevent strain on the shoulder joint and reduce the risk of injury.
- Warm Up Before Exercise: Engaging in a proper warm-up routine before physical activity can help prepare the muscles and tendons for movement, reducing the risk of injury.
- Gradually Increase Intensity: Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of exercise can help prevent overuse injuries to the shoulder joint.
- Use Proper Technique: When engaging in activities that involve overhead movements, such as sports or weightlifting, using proper technique can help reduce strain on the shoulder tendons.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help keep the tendons hydrated and flexible, reducing the risk of injury.
Conclusion:
Calcific tendonitis in the shoulder joint can be a painful and debilitating condition, but with proper understanding and management, individuals can effectively alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence. By addressing the underlying causes, seeking appropriate treatment, and adopting preventive measures, individuals can maintain shoulder health and function optimally in their daily lives.
FAQ’s :
Are calcium deposits on the shoulder serious?
Calcium deposits on the shoulder, also known as calcific tendonitis, aren’t necessarily serious. In many cases, they don’t cause any problems. However, if the deposits become large or inflamed, they can cause significant pain and limit your shoulder movement.
How do I get rid of calcification on my shoulder naturally?
While there’s no guaranteed natural cure for shoulder calcification, some approaches may help manage symptoms and potentially promote healing. However, it’s important to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Here are some options to discuss with your doctor:
- Rest and Ice: Reducing activity that aggravates the shoulder and applying ice packs to the area can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Physical Therapy: Specific exercises can improve shoulder mobility, strengthen supporting muscles, and potentially aid in breaking down the calcium deposits.
- Anti-inflammatory supplements: Supplements like turmeric or bromelain may offer some relief, but discuss with your doctor to ensure they don’t interact with any medications you’re taking.
Important to remember:
- These approaches may take time to show improvement.
- They might not work for everyone, and some cases might require medical intervention.
Does massage help shoulder calcification?
Massage can be a helpful tool in managing pain associated with shoulder calcification, but it won’t directly break down the calcium deposits. Here’s a breakdown of how massage can help:
- Pain Relief: Massage therapy can help relax muscles surrounding the shoulder joint, which can reduce pain and tension.
- Improved Circulation: Massage can improve blood flow to the area, which can promote healing and reduce inflammation.
- Increased Range of Motion: Gentle massage and stretching techniques can help improve flexibility and range of motion in the shoulder joint.
However, it’s important to note that deep tissue massage directly on the area with calcification is not recommended. It can irritate the tendon and worsen the pain.
I am a highly skilled and experienced content writer with a Doctorate in Therapy degree. With a deep understanding of the human body and a passion for health and wellness. I combines my clinical expertise and writing skills to create valuable and engaging content.